Introduction
In today's technologically advanced world, the prevalence of electronic devices and communication systems is greater than ever. As these devices become more sophisticated, the need for reliable communication and data integrity has risen correspondingly. One of the major challenges in ensuring optimal performance in electronic systems is electromagnetic interference (EMI). This article explores the importance of shielded cables in mitigating EMI, highlighting their construction, applications, and benefits in various industries.
Understanding Electromagnetic Interference (EMI)
Electromagnetic interference (EMI) refers to the disruption of the normal operation of electronic devices due to electromagnetic fields. These fields can be generated by a variety of sources, including:
- Natural Sources: Lightning, solar flares, and cosmic radiation.
- Artificial Sources: Electrical equipment, motors, radio transmitters, and wireless devices.
Types of EMI
EMI can be classified into two primary types:
- Radiated Interference: This occurs when electromagnetic fields propagate through the air and affect nearby electronic devices.
- Conducted Interference: This type happens when unwanted signals travel along power lines or communication cables, disrupting the operation of connected devices.
Both types of interference can result in data loss, equipment malfunction, and degraded system performance.
The Role of Shielded Cables
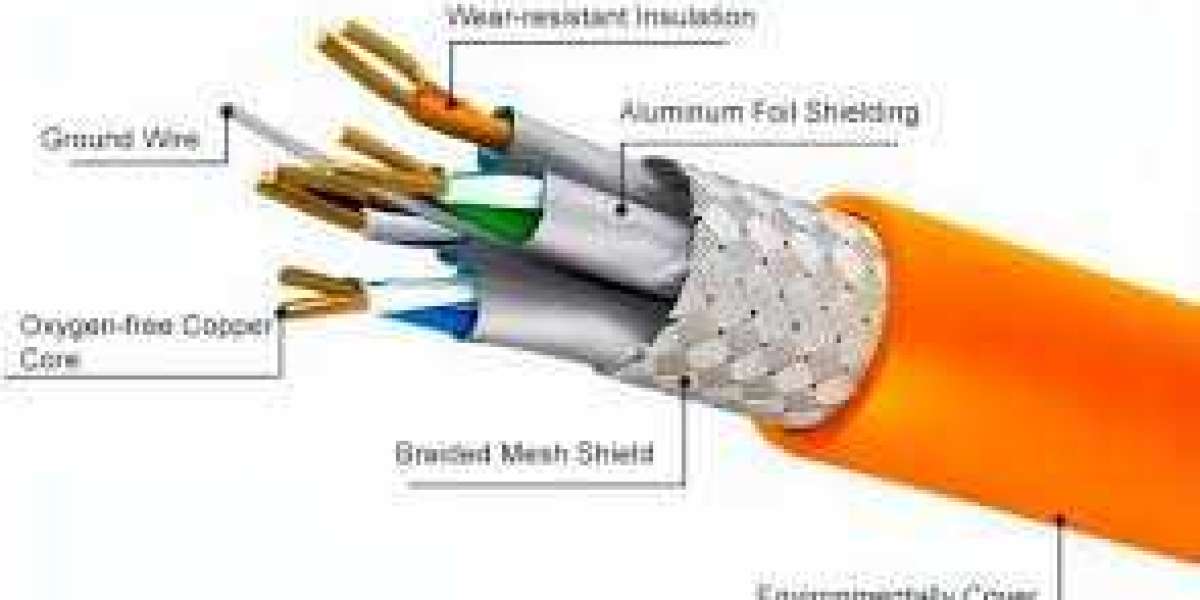
Shielded cables are specifically designed to protect against EMI by incorporating a protective layer around the conductors. This layer is typically made from materials such as foil or braided metal mesh, which serves as a barrier against external electromagnetic fields. The construction of shielded cables can vary, but they generally include the following components:
- Conductors: These carry the electrical signals. They can be either twisted pairs or coaxial wires, depending on the application.
- Insulation: This layer surrounds the conductors and prevents short circuits and electrical leakage.
- Shielding: This protective layer is crucial for reducing EMI. It can be made from various materials, including aluminum foil, copper wire, or a combination of both.
- Outer Jacket: This layer provides physical protection to the cable, ensuring durability and resistance to environmental factors.
How Shielding Works
Shielding works by reflecting and absorbing electromagnetic waves. When an external electromagnetic field encounters the shield, the conductive material creates a barrier that redirects the interference away from the conductors inside the cable. This results in a significant reduction in the level of EMI that can affect the signal integrity.
Benefits of Shielded Cables
1. Enhanced Signal Integrity
One of the primary advantages of using shielded cables is their ability to maintain signal integrity. By minimizing the effects of EMI, shielded cables ensure that data transmission is reliable and accurate. This is especially crucial in applications where high-speed data transfer is required, such as in computer networks and telecommunications.
2. Reduced Noise and Crosstalk
Crosstalk is the unwanted transfer of signals between communication channels, which can lead to data corruption and reduced performance. Shielded cables help to minimize crosstalk by providing a protective barrier that reduces the likelihood of signal interference. This is particularly important in environments with multiple data lines running in close proximity to each other.
3. Increased System Reliability
In industries where equipment reliability is critical—such as healthcare, aviation, and manufacturing—shielded cables play a vital role in ensuring uninterrupted operation. By protecting against EMI, these cables help prevent malfunctions that could lead to costly downtime or safety hazards.
4. Compliance with Regulatory Standards
Many industries have stringent regulations regarding EMI and signal integrity. Using shielded cables can help organizations comply with these standards, ensuring that their equipment meets the necessary requirements for electromagnetic compatibility (EMC). This compliance can be critical for avoiding fines and maintaining a positive reputation.
5. Improved Performance in Challenging Environments
Shielded cables are particularly beneficial in environments with high levels of EMI, such as industrial settings, data centers, and urban areas with dense electronic activity. In these environments, the use of shielded cables can significantly enhance the performance and reliability of electronic systems.
Applications of Shielded Cables
1. Telecommunications
In telecommunications, shielded cables are essential for maintaining the quality of voice and data transmission. They help reduce interference from external sources, ensuring clear communication and reliable data transfer.
2. Networking
In data networking, shielded twisted pair (STP) cables are commonly used to minimize crosstalk and external interference. These cables are crucial for high-speed data transfer in local area networks (LANs) and are often found in data centers and server rooms.
3. Industrial Automation
In industrial environments, shielded cables are used to connect sensors, actuators, and control systems. The presence of heavy machinery and electrical equipment can generate significant EMI, making shielded cables essential for maintaining system integrity.
4. Audio and Video Equipment
Shielded cables are commonly used in audio and video applications to prevent signal degradation and maintain high-quality sound and image transmission. They are often used in professional audio equipment, broadcasting, and home theater systems.
5. Medical Devices
In healthcare settings, shielded cables are critical for connecting medical devices and equipment. They help prevent interference that could compromise patient safety and the accuracy of medical diagnostics.
Choosing the Right Shielded Cable
When selecting shielded cables for a specific application, several factors should be considered:
1. Type of Shielding
Different types of shielding provide varying levels of protection against EMI. Common types include:
- Foil Shielding: Offers good protection against high-frequency interference and is often used in applications where flexibility is essential.
- Braided Shielding: Provides excellent coverage and is ideal for environments with heavy machinery and electrical activity.
2. Cable Construction
Consider the construction of the cable, including the number of conductors, insulation materials, and the overall design. For instance, twisted pair cables are often preferred in networking applications due to their ability to minimize crosstalk.
3. Environmental Factors
Evaluate the environmental conditions in which the cable will be used. Factors such as temperature, humidity, and exposure to chemicals can influence the choice of cable. Ensure that the selected cable is rated for the specific conditions of the installation site.
4. Compliance with Standards
Ensure that the selected shielded cable meets the necessary industry standards for electromagnetic compatibility (EMC). This can be particularly important in regulated industries such as telecommunications and healthcare.
Conclusion
Shielded cables play a crucial role in reducing electromagnetic interference and ensuring the reliable performance of electronic systems. With the increasing prevalence of electronic devices and the growing complexity of communication networks, the importance of shielded cables cannot be overstated. By minimizing EMI, these cables enhance signal integrity, reduce noise and crosstalk, and improve overall system reliability. In a world where uninterrupted communication is vital, investing in high-quality shielded cables is essential for organizations across various industries.